Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Adult: Each tab contains vildagliptin (mg)/metformin (mg): 50/500, 50/850, or 50/1,000: 1 tab bid based on patient’s current regimen, effectiveness, and tolerability. Max: Vildagliptin: 100 mg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Type 2 diabetes mellitus Adult: Each tab contains vildagliptin (mg)/metformin (mg): 50/500, 50/850, or 50/1,000: 1 tab bid based on patient’s current regimen, effectiveness, and tolerability. Max: Vildagliptin: 100 mg daily.
|
|
Renal Impairment
Severe (GFR <30 mL/min): Contraindicated.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food. Take w/ or immediately after meals to reduce GI discomfort.
|
|
Contraindications
Acute metabolic acidosis (e.g. lactic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis); conditions which may alter renal function (dehydration, severe infection, shock); acute or chronic disease which may cause tissue hypoxia (e.g. cardiac or resp failure, recent MI, shock); undergoing surgery. Acute alcohol intoxication. Lactation. Severe hepatic and renal (GFR <30 mL/min) impairment. Intravascular admin of iodinated contrast agents.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ history of acute pancreatitis. Mild to moderate renal impairment. Pregnancy. Not intended for the treatment of type 1 DM and diabetic ketoacidosis.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Dehydration, acute pancreatitis, bullous and exfoliative skin lesions, decreased vit B12 levels, hypoglycaemia. Rarely, hepatic dysfunction (i.e. hepatitis).
Nervous: Dizziness, tremor, headache, fatigue. GI: Nausea, diarrhoea. Dermatologic: Hyperhidrosis. Potentially Fatal: Rarely, lactic acidosis. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor LFTs prior to initiation, during treatment at 3-mth intervals during the 1st yr, and periodically thereafter; and renal function regularly.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Delayed elimination of metformin w/ cationic active substances eliminated by renal tubular secretion (e.g. cimetidine). Increased risk of lactic acidosis w/ ACE inhibitors, angiotension receptor antagonists, diuretics, NSAIDs. Increased risk of angioedema w/ ACE inhibitors. Thiazide diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, OC, sympathomimetics, phenytoin, niacin, Ca channel blockers and isoniazid may exacerbate loss of glycaemic control.
Potentially Fatal: Intravascular admin of iodinated contrast agents may cause contrast-induced nephropathy, leading to increased risk of lactic acidosis. |
|
Food Interaction
Food decreases the extent and slightly delays absorption. Increased risk of lactic acidosis w/ alcohol.
|
|
Action
Description: Metformin is a biguanide antidiabetic agent that decreases hepatic glucose production via inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, improves peripheral utilisation and uptake of glucose by increasing insulin sensitivity, and delays intestinal glucose absorption. Vildagliptin is an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), thereby increasing the concentration of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). This enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and reduces glucagon production.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Metformin: Slowly and incompletely absorbed from the GI tract. Absolute bioavailability: Approx 50-60%. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 2.5 hr. Vildagliptin: Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability: 85%. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 1.7 hr. Distribution: Metformin: Partitions into erythrocytes; crosses the placenta and enters breast milk in small amounts. Volume of distribution: 63-276 L. Vildagliptin: Distributed equally between plasma and RBCs. Plasma protein binding: 9.3%. Metabolism: Vildagliptin: Metabolised (69%) in the kidney via hydrolysis into the major inactive metabolite, LAY-151. Excretion: Metformin: Via urine (90% as unchanged drug). Terminal elimination half-life: Approx 6.5 hr. Vildagliptin: Via urine (85%, 23% as unchanged drug) and faeces (15%). Elimination half-life: Approx 3 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
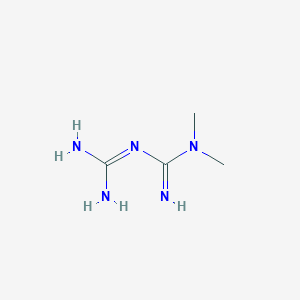 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Metformin, CID=4091, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Metformin (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) 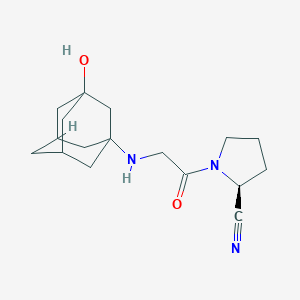 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Vildagliptin, CID=6918537, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Vildagliptin (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from moisture.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
A10BD08 - metformin and vildagliptin ; Belongs to the class of combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs. Used in the treatment of diabetes.
|
|
References
Anon. Metformin. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 15/06/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Metformin Hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 15/06/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Vildagliptin. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 15/06/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Vildagliptin with Metformin. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 15/06/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Metformin Hydrochloride. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 15/06/2017.
|